
NATIONAL FLOOD FORECASTING AND WARNING PROGRAM
INTRODUCTION
The National Flood Forecasting and Warning Program (PRAB) has been created following the massive floods that occurred in December 2014 which hit 8 states namely Kelantan, Terengganu, Pahang, Perak, Perlis, Johor, Sabah and Sarawak. The flood has recorded a total of 25 deaths with more than 500,000 evacuated and the cost of destruction exceeded RM 2.85 billion.
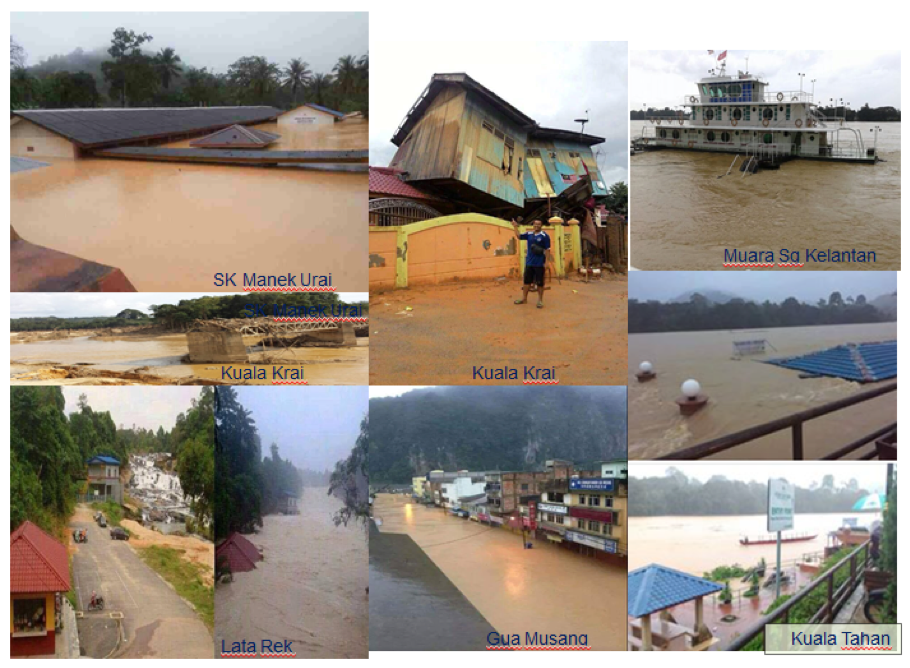

Figure 1: Pictures of December 2014 flood events in Kelantan, Terengganu and Pahang States
Based on the study carried out by Department of Irrigation and Drainage Malaysia (JPS), Updating of Condition of Flooding and Flood Damage Assessment in Malaysia, 2012 found that 10.1% of the country’s total area is a flood-prone area with nearly 5.67 million people affected by floods. Its impact leads to a loss of property exceeding RM 1.0 Billion a year.
The PRAB program will be implemented comprehensively throughout the country which will involve flood prediction models in 41 major river basins. This program is expected to have a direct positive impact on the flood victims.
OBJECTIVES
The PRAB program has set four key objectives to be achieved: –
- To develop a system that can forecast monsoon flood 7 days earlier based on weather forecast data from the Malaysia Meteorological Department.
- To increase the capacity of the existing system for warning and dissemination of monsoon flood from 6 hours to 2 days earlier for the benefit of related agencies and population affected by the flood
- To increase accuracy of flood forecasting by reducing the difference between forecast and observed data from 1 meter water level to less than 0.5 meter
- To develop a system that’s capable to forecast and disseminate flash flood warning to public from1 to 3 hours earlier based on weather forecast data from Malaysia Meteorological Data Department focused on river overflow.
MAIN COMPONENT
To achieve the PRAB objective program, there are four (4) major components that will be implemented in an integrated manner using the latest technology. The components are as follows:
- Hydrological Data Detection System
- Database and ICT Infrastructure System
- Flood Modeling and Forecasting System
- Flood Warning and Dissemination System
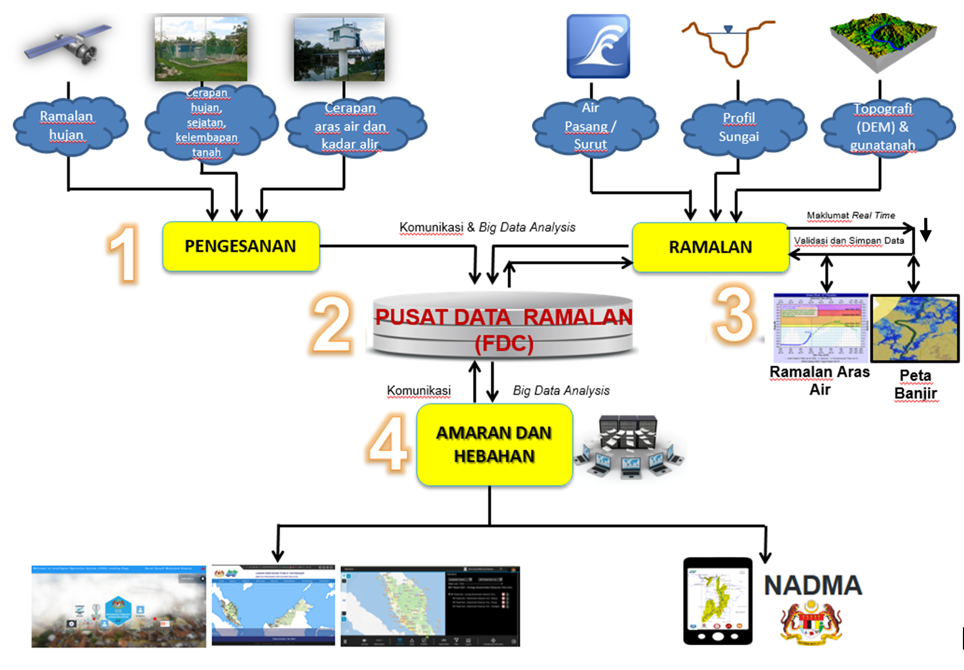
Figure 2: PRAB’s main components
Implementation
The PRAB program is implemented in two phases namely PRAB Phase 1 and PRAB Phase 2. It will be implemented within 10 years (2015 to 2025) where for PRAB Phase 1 Project (PRABF1) has been implemented for three (3) major river basins namely Sg. Kelantan, Sg. Terengganu and Sg. Pahang. For the PRAB Phase 2 Project, it started in 2018 and is expected to be completed by 2025. PRAB Phase 2 will involve flood forecasting models in 38 river basins nationwide including Sabah and Sarawak.

Figure 3: River basin location is involved in PRAB
FLOOD WARNING AND WARNING TRANSFORMATION
The PRAB program has targeted to transform the existing flood forecast and warning system to be more advance and a bigger impact to the public
There are four main elements in the transformation which is;
- Early flood forecast duration
- Early flood warning duration
- Enhanced the flood warning database system
- Wider coverage of flood warning dissemination
The transformation of the four elements can be described as in Figure 4.

The transformation of the four elements can be described as in Figure 4.
INTEREST AND BENEFITS
There are five main benefits to the PRAB program:
- Provide sufficient time for agencies and residents to act early in the flood
- Reduces the loss of public and government property
- Increase the public confidence level to the government delivery system
- Allowing agencies to coordinate logistics and displacement strategies more efficiently and efficiently
- Improve the disaster agencies ability to plan and execute flood evacuation more organize and timely.
Planning and Strategy Unit
National Flood Forecasting and Warning Centre (PRABN)
Department of Irrigation and Drainage, Malaysia

